Sociology is a popular optional for the Civil Services Exam conducted by Union Public Service Commission. One of the important reasons for the popularity of sociology as an optional is that the UPSC Sociology syllabus is quite short in comparison to most other optional subjects.
An Overview
Sociology syllabus is divided into 2 papers - Paper 1 and Paper 2. While Sociology Paper 1 deals with the Fundamentals of Sociology, its Paper 2 deals with our own (Indian) society. To go through the Sociology optional syllabus in detail, download or read it below.
PAPER - I
FUNDAMENTALS OF SOCIOLOGY
- (a) Karl Marx
- (b) Emile Durkheim
- Division of labour
- Social facts
- Criticism of social fact theory
- Suicide
- (d) Talcott Parsons
- Social system and its functional pre requisites
- AGIL paradigm and its corresponding systems
- Pattern variables and its criticism
- Cybernatic Hierarchy of control Moving Equilibrium
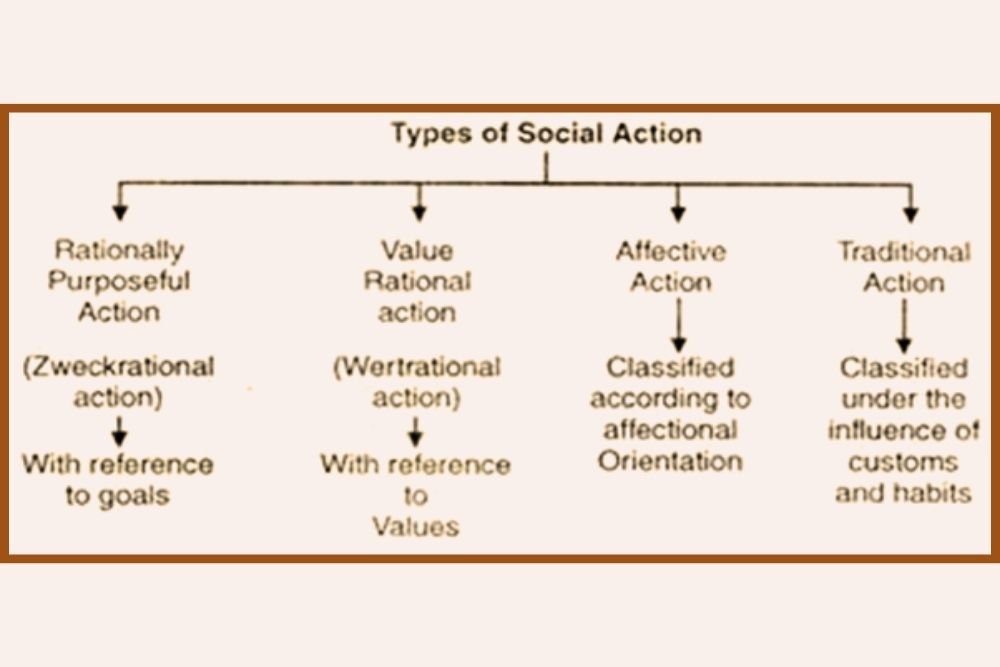
- Social actions
- (e) Robert K. Merton
- Manifest and Latent functions
- Reference Groups
- Anticipatory socialisation
- Conformity and deviance
- Forms of Deviance(Homosexuality etc)
- (f) Mead-Self and identity
- Self Stages of socialisation Generalised other Identity: and Me Symbolic Interactionism Criticism
- (a) Concepts
- Equality,
- Inequality
- Hierarchy
- Vertical and Horizontal mobility
- Social Exclusion and its types
- Deprivation Poverty and its theories
- Solutions to tackle poverty
- Deprivation.
- (b) Theories of social stratification
- Structural functionalist theory
- Marxist theory
- Weberian theory
- (c) Dimensions
- Social stratification of class
- status groups
- Gender
- Ethnicity
- Race
- (d) Social mobility
- Open and closed systems,
- Types of mobility,
- Sources and causes of mobility
- Social organization of work in different types of society - slave society, feudal society, industrial capitalist society
- Formal and informal organization of work.
- Gig Economy
- Self Help groups
- Alienation of workers
- Feminization of labour
- Human Relations school by Elton Mayo
- Labour and society
- Ideology and Identity politics
- Sociological theories of power
- Types of power
- Power elite,Circulation of Elites,Modern Elite theory.Pluralism
- Bureaucracy
- Functions and dysfunctions Formal and informal structure of bureaucracy
- Pressure groups and Political parties
- Nation, state, citizenship, democracy, civil society, ideology
- Protest, agitation
- Social movements (theories of social movements, life cycle of movements, Challenges faced by social movements, New social movements, Millenarian movement)
- Collective action, revolution
- Sociological theories of religion
- Functionalist
- Marxist
- Feminist Weber' perspective(Protestant ethics) and criticism
- Symbolic interactionists
- Types of religious practices: animism, monism, pluralism, sects, cults
- Religion in modern society
- Functions and dysfunctions of religion
- Sects and Cults
- Secularization
- Religious revivalism
- Fundamentalism
- Religious pluralism
- Corelation between religion and science
- Family, household, marriage
- Scholarly views on family(Functionalist view marxist view,feminist view etc)
- Changes in family structures after Industrialization
- Types and forms of family
- Lineage and descent
- Patriarchy and sexual division of labour
- Patriarchal bargain
- Feminist ideas to deal with patriarchy
- Contemporary trends
- Relevance of marriage in current times Different types of marriage Increased divorce rates
- Sociological theories of social change. (Functional,post modernist,conflict, evolutionary theories like Social darwinism and cyclical theories)
- Development and dependency.(Metro satellite model, World system theory of Wallerstein, Development of underdevelopment)
- Agents of social change
- Education and social change
- Science, technology, and social change
- Cultural lag
- Nationalism, Citizenship, Civil society
- Globalization and Modernization
- Social media, its advantages and disadvantages, Social media activism
- Digital Divide
Download Sociology UPSC Syllabus PDF
Syllabus of Paper -2